News!
December 27th, 2023: New Release of DISGENET plus (version 24)
The current version of DISGENET plus (v24) contains 1,770,610 gene-disease associations (GDAs), between 25,992 genes and 39,644 diseases and traits; 1,119,130 variant-disease associations (VDAs), between 616,660 variants and 16,605 diseases and traits, and over 45 M disease-disease associations. DISGENET plus also contains more than 280,000 associations involving 12,000 diseases that have been detected in animal models. This release provides annotations for 3,530 chemicals associated with GDAs and VDAs. 1,425,789 publications support the GDAs, and 158,269 publications support the VDAs. In total, DISGENET plus contains a corpus of 1,434,206 publications that support the genotype-phenotype associations.
What is new on the database?
- -New data source: Rat Genome Database
- -17% increase in the number of GDAs compared to v21: more than 260K new GDAs available
- -Increased coverage of genes and diseases/phenotypes: more than 1.3K new genes and 3.2K diseases and phenotypes incorporated in the database
- -New attributes for variants: we provide the SIFT and PolyPhen scores for pathogenicity for each variant
What is new on the platform?
– New features in the disgenetplus2r package (version 1.0.3):
-
- -New features:
- -Queries with functions disease2variant, chemical2variant, and chemical2vda now can receive SIFT and POLYPHEN ranges
- -Documentation:
- -NEWS.md file was added to document package changes
- -All functions that use the parameter database now have all data sources, including RGD and MGD, that are new sources
- -Bug fixes:
- -Functions that use the parameter database that query variant endpoints now throw an error if a database is not GWASCAT, CLINVAR, UNIPROT, TEXTMINING_HUMAN, CURATED, or ALL
- -New features:
September 27th, 2023: New Release of DISGENET plus (version 23)
The current version of DISGENET plus (v23) contains 1,729,483 gene-disease associations (GDAs), between 25,869 genes and 39,141 diseases and traits; 1,117,115 variant-disease associations (VDAs), between 617,724 variants and 16,533 diseases and traits, and over 43M disease-disease associations. DISGENET plus also contains more than 1,7 M associations involving 14,000 diseases that have been detected in animal models. This release provides annotations for 3,507 chemicals associated with GDAs and VDAs. 1,399,652 publications support the GDAs, and 156,684 publications support the VDAs. In total, DISGENET plus contains a corpus of 1,408,123 publications that support the genotype-phenotype associations.
What is new on the database?
- – New data source: Mouse Genome Database
- – 10% increase in the number of GDAs: more than 175K new GDAs available
- – Increased coverage of genes and diseases/phenotypes: almost 2.5K new diseases and phenotypes incorporated into the database
- – Changes in the Association type ontology
What is new on the platform?
– New features in the disgenetplus2r package:
-
- – Changes in the plot function to enable visualization by DiseaseClass and ProteinClass both in networks and heatmaps.
- – Heatmaps available for download as png and json files
- – Customization of network plots using the visNetwork package.
- – Retrieval of DDAs by relationship types.
July 17th, 2023: Our work featured by the Innovative Health Initiative
The Innovative Health Initiative has featured our new text mining technology for mining information on clinical biomarkers in a news article.
This work was carried out in the context of the eTRANSAFE project and has been published in the Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal this year.
The dataset on Clinical Biomarkers is already available within the DISGENET plus platform. Contact us if you want to learn more about the clinical biomarker dataset.
Citation
Janet Piñero, Pablo S. Rodriguez Fraga, Jordi Valls-Margarit, Francesco Ronzano, Pablo Accuosto, Ricard Lambea Jane, Ferran Sanz, Laura I. Furlong. Genomic and proteomic biomarker landscape in clinical trials. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, Volume 21, 2023, Pages 2110-2118, ISSN 2001-0370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2023.03.014
July 5th, 2023: New Release of DISGENET plus (version 22)
The current version of DISGENET plus (v22) contains 1,552,626 gene-disease associations (GDAs), between 25,474 genes and 36,675 diseases and traits; 1,115,471 variant-disease associations (VDAs), between 610,272 variants and 16,168 diseases and traits, and over 32,7 M disease-disease associations. DISGENET plus also contains more than 250,000 associations involving 12,000 diseases that have been detected in animal models. This release provides annotations for 3,173 chemicals associated with GDAs and VDAs. 1,107,571 publications support the GDAs, and 155,495 publications support the VDAs. In total, DISGENET plus contains a corpus of 1,160,823 publications that support the genotype-phenotype associations.
What is new on the database?
-New associations: more than 40K new GDAs and VDAs are available, increasing the coverage of genes, variants and diseases.
-New feature for DDAs: semantic relations from the UMLS between diseases, to learn more about the relation between diseases and phenotypes.
What is new on the platform?
-New features on the REST API:
-New endpoint to search for chemicals, to retrieve information on the number of GDAs, VDAs and supporting publications.
-Search by chemical available on the endpoints GDA summary & evidence, VDA summary & evidence.
-New features on the disgenetplus2r package:
-New functions to search for chemicals and their associated GDAs and VDAs New functions to search for chemicals and their associated genes, variants and diseases.
-Different visualizations are available for the new functions.
For more information, visit our YouTube Channel with short videos on using the web platform and exploiting its functionalities.
June 23th, 2023: Innovative SME seal
We have achieved the Innovative SME seal, a recognition given to small and medium-sized enterprises with an innovative character. The Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation grants this distinction to reward those SMEs with great activity in R&D.
June 16th, 2023: RISKHUNT3R 4th General Assembly Meeting
This week we joined the RISK-HUNT3R Stakeholder Symposium and the 4th General Assembly Meeting meeting at Egmond aan zee, The Netherlands.
Our team members Jaione Telleria Zufiaur, Jordi Valls Margarit and Laura I. Furlong presented our solutions to promote innovation in chemical risk assessment leveraging AI, genomics and network science.
June 14th, 2023: New publication on the eTRANSAFE project on Nature Reviews Drug Discovery
We are proud to be part of the eTRANSAFE initiative to empower translational safety assessment with data science. Check out the new publication in Nature Reviews Drug Discovery presenting the major achievements of the project:
 Sanz, F., Pognan, F., Steger-Hartmann, T., Díaz, C., Asakura, S., Amberg, A., … & Wilkinson, D. (2023). eTRANSAFE: data science to empower translational safety assessment. Nature reviews. Drug Discovery. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41573-023-00099-5
Sanz, F., Pognan, F., Steger-Hartmann, T., Díaz, C., Asakura, S., Amberg, A., … & Wilkinson, D. (2023). eTRANSAFE: data science to empower translational safety assessment. Nature reviews. Drug Discovery. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41573-023-00099-5
At Medbioinformatics we have contributed with our text mining and bioinformatic expertise to develop a new database of clinical biomarkers, new text mining tools to extract information from legacy pre-clinical toxicology reports and novel methodologies to identify safety mechanistic biomarkers.
To learn more about our developments check out these publications or contact us!
Piñero, J., Fraga, P. S. R., Valls-Margarit, J., Ronzano, F., Accuosto, P., Jane, R. L., … & Furlong, L. I. (2023). Genomic and proteomic biomarker landscape in clinical trials. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 21, 2110-2118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2023.03.014
Callegaro, G., Kunnen, S. J., Trairatphisan, P., Grosdidier, S., Niemeijer, M., den Hollander, W., … & van de Water, B. (2021). The human hepatocyte TXG-MAPr: gene co-expression network modules to support mechanism-based risk assessment. Archives of toxicology, 95, 3745-3775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-03141-w
March 30th, 2023: New Release of DISGENET plus (version 21)
The current version of DISGENET plus (v21) contains 1,509,314 gene-disease associations (GDAs), between 24,613 genes and 36,319 diseases and traits; 1,070,721 variant-disease associations (VDAs), between 584,693 variants and 16,010 diseases and traits, and over 32 M disease-disease associations. DISGENET plus also contains more than 240,000 associations involving 12,000 diseases detected in animal models. This release provides annotations for 3,174 chemicals associated with GDAs and VDAs. The GDAs are supported by 1,105,030 publications, and the VDAs by 141,088 publications.
What is new on the database?
-New information on chemicals associated with GDAs and VDAs. We identify mentions of chemicals by text mining within the publications that support the GDAs and VDAs.
-New attribute for genes: annotations to pathways from Reactome.
-New data source for VDAs: PheWas Catalog (https://phewascatalog.org/).
-New attribute for VDAs: annotation of the effect of the variant on the phenotype, such as gain of function (GoF) or loss of function (LoF) mutations. This information is obtained by text mining.
-All data sources updated, including the text mining results and the disease and gene ontologies.
What is new on the platform?
- New features on the web platform:
New feature: example searches available to unregistered users. To show the functionalities of the web platform to a wider audience, we have performed changes in the platform to enable users to perform searches without the need to register for a trial account.
Check the following examples for:
-Diseases: Obesity Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
-Variants: rs121913279 rs35705950
-Drugs/Chemicals: streptozocin imiquimod
These searches show a subset of the available results (up to 30 results) and limited functionality of the platform. To get full access to all the results and enjoy all the functionalities of the platform, users should enter with their user credentials.
- User access and user profile:
-Authentication by the user’s email address
-User profile with easy access to API key, web tour and password recovery
- New features on the REST API
-Search by GoF/LoF variations and consequence type in the “VDA evidence” endpoint.
-Search by consequence type in the “VDA summary” endpoint.
For more information, visit our YouTube Channel with short videos on how to use the web platform and exploit its functionalities.
For examples of applications check out the latest entries in our blog:
-
- Genetics for drug and chemical risk assessment Blog entry
- Genetic support for FDA drug approvals in 2021 Blog entry
- Report on the analysis of FDA drug approvals with data from DISGENET plus
March 20, 2023: Our new publication, "Genomic and proteomic biomarker landscape in clinical trials” is available in the Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.
The use of molecular biomarkers to support disease diagnosis, monitor its progression, and guide drug treatment has gained traction in the last decades. While only a dozen biomarkers have been approved for their exploitation in the clinic, many more are evaluated in the context of translational research and clinical trials. But the information on which biomarkers are measured, for which purpose, and in relation to which conditions are not readily accessible: biomarkers used in clinical studies are described as free text, posing significant challenges in finding, analyzing, and processing data on biomarkers by both humans and machines.
We developed a text-mining approach to identify proteomic and genomic biomarkers used in clinical trials and classify them according to the methodologies by which they are measured. Our approach is the first of this kind and is presented as a proof of concept of the information that can be extracted and standardized to facilitate access to knowledge on the use of biomarkers in clinical studies.
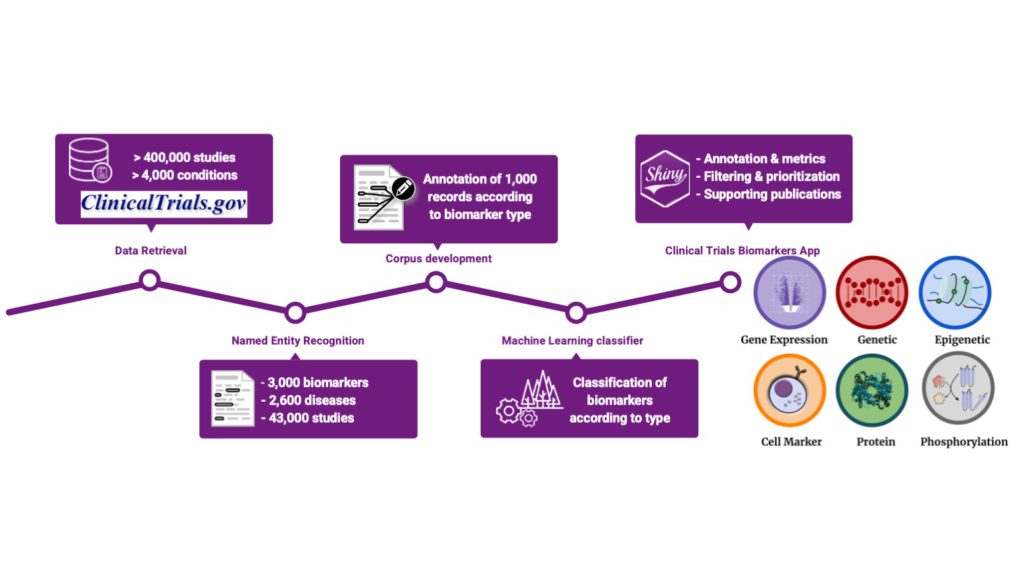
Extracting and structuring information on biomarkers’ use in clinical studies enabled us to perform a trend analysis covering different aspects of biomarkers’ use. One interesting observation was the striking contrast between the number of biomarkers evaluated in clinical studies and the number of biomarkers currently approved by the FDA, underlying the need to accelerate biomarker approval by regulatory agencies. We aim at facilitating this process by identifying and structuring the information on biomarkers’ use in clinical studies.
Information on clinical biomarkers is integrated in our DISGENET plus platform.
If you want to learn more, here is the link to the publication:
Janet Piñero, Pablo S. Rodriguez Fraga, Jordi Valls-Margarit, Francesco Ronzano, Pablo Accuosto, Ricard Lambea Jane, Ferran Sanz, Laura I. Furlong. Genomic and proteomic biomarker landscape in clinical trials. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, Volume 21, 2023, Pages 2110-2118, ISSN 2001-0370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2023.03.014
March 14-15, 2023: Advanced therapies 2023
We attended Advanced Therapies 2023 at ExCel, London, to present our knowledge platform on disease genomics DISGENET plus and our text mining and systems toxicology approaches to support novel gene and cell therapy development.
February 22-23, 2023: eTRANSAFE closing event
We joined the eTRANSAFE final event “Towards a quantum leap in drug safety assessment” in Sitges (Spain). One of our contributions to the project includes the application of AI to identify biomarker information from clinical studies and make this information ready to use for other applications in drug safety and precision medicine. Information on clinical biomarkers is already integrated within our DISGENET plus platform.
February 13-16, 2023: RISKHUNT3R 3rd General Assembly Meeting
Our team members Jordi Valls and Laura I. Furlong attended the 3rd RISKHUNT3R General Assembly and Steering Team meeting in Egmond aan Zee (The Netherlands).
The last four days have been dedicated to training events, reviewing the work done, and planning the next steps to develop. Our team presented our contributions to Next Generation Risk Assessment, including the tool Chemical Effect Predictor.
January 23rd, 2023: Release of version 20.1 of DISGENET plus
A new release of DISGENET plus (v20.1) is available online. Please visit it at https://www.disgenetplus.com/ and try the new features.
The current version of DISGENET plus (v20.1) contains 1,516,952 gene-disease associations (GDAs), between 24,642 genes and 34,124 diseases and traits; 1,009,638 variant-disease associations (VDAs), between 578,771 variants and 15,185 diseases and traits, and over 30,421,348 M disease-disease associations. DISGENET plus also contains more than 250,000 associations involving 11,000 diseases detected in animal models. This release provides annotations for 3,937 chemicals associated with GDAs and VDAs.
- New information on chemicals associated with GDAs and VDAs: we identify mentions through chemicals by text mining within the publications that support the GDAs and VDAs.
- New attribute for genes: annotations to pathways from Reactome.
- New attribute for VDAs: annotation of the effect of the variant on the phenotype, such as gain of function (GoF) or loss of function (LoF) mutations. This information is obtained by text mining.
November 3rd, 2022: Release of version 20.0 of DISGENET plus
A new release of DISGENET plus (v20) is available online. Please visit it at https://www.disgenetplus.com/ and try the new features.
The current version of DISGENET plus (v20) contains 1,517,357 gene-disease associations (GDAs), between 24,643 genes and 34,158 diseases, disorders, traits, and clinical or abnormal human phenotypes, 1,010,102 variant-disease associations (VDAs), between 578,958 variants and 15,209 diseases, traits, and phenotypes and over 47 M disease-disease associations. DISGENET plus also contains more than 250,000 associations involving 11,000 diseases that have been detected in animal models.
- All data sources updated
- Increased coverage for variants: 13,900 new variants, 40,000 new VDAs compared to the previous release
- 30,000 new GDAs
- New: reported odds ratio or beta-coefficient associated with the GWAS study are now available
- New: disease-disease associations can be filtered by p values of the Jaccard index of genes and variants
- New feature: visualization of the data is available (bar plots, heatmaps, and networks)
June 27th, 2022: Release of version 19.0 of DISGENET plus
A new release of DISGENET plus (v19) is available online. Please visit it at https://www.disgenetplus.com/ and try the new features.
The current version of DISGENET plus (v19) contains 1,483,670 gene-disease associations (GDAs), between 24,249 genes and 34,041 diseases, disorders, traits, and clinical or abnormal human phenotypes and 968,761 variant-disease associations (VDAs), between 564,982 variants and 15,059 diseases, traits, and phenotypes and over 46 M disease-disease associations. DISGENET plus also contains more than 260,000 associations involving 11,000 diseases that have been detected in animal models.
- All data sources updated
- Increased coverage for variants: 12,000 new variants, 35,000 new VDAs compared to the previous release
- 100,000 new GDAs
- New: searches by aminoacid-position are now available for variants
- New: now users can filter genes using the gene type!
- New: links to clinical trials are now available for genes and diseases
March 15th, 2022: Release of version 18.0 of DISGENET plus
A new release of DISGENET plus (v18) is available online. Please visit it at https://www.disgenetplus.com/ and try the new features.
The version v18 of DISGENET plus contains 1,371,161 gene-disease associations (GDAs), between 23,111 genes and 32,630 diseases, disorders, traits, and clinical or abnormal human phenotypes and 933,409 variant-disease associations (VDAs), between 552,680 variants and 14,626 diseases, traits, and phenotypes, and over 41 M disease-disease associations. This new release also contains more than 200,000 associations involving 10,000 diseases that have been detected in animal models.
Our database now summarizes the disease genomics knowledge from over 1M scientific publications by mining 30M publications.
- All data sources updated
- Increased coverage for variants: 28% more variants, 23% more VDAs compared to the previous release
- 13% more pieces of evidence for GDAs
November 22th, 2021: Release of the web interface
We are proud to release our new web interface, available at https://www.disgenetplus.com/
Visit it and register for a free trial!
November 11th, 2021: Release of version 17 of DISGENET plus
The version 17 of disgenet plus contains 1,256,954 gene-disease associations between 22,703 genes and 31,781 diseases, disorders, traits, and clinical or abnormal human phenotypes, 648,990 variant-disease associations between 375,441 variants and 14,276 diseases, traits, and phenotypes and 36,040,896 disease-disease associations. DISGENET plus contains information that comprises 855,346 scientific publications.
- All data sources updated
- New association types: chemical response, protective variant, and variant of uncertain significance
A new release of the DISGENET plus REST API is available!
September 16th, 2021. New release of the DISGENET plus REST API
We are thrilled to announce the new version of the DISGENET plus REST API, that provides different ways to interrogate the DISGENET plus database.
The main features of the new release are:
-New endpoints for the retrieval of attributes for genes, diseases, variants and publications;
-New endpoints to retrieve the summary and the evidences for the associations (GDAs and VDAs);
-Free text search support in the gene and disease entity endpoints, useful to recover database identifiers from free text expressions (e.g., to obtain the UMLS identifiers for the string “schizophrenia”);
-Protein class information added in the response of the GDA endpoints (summary and evidence).
We expect these changes ease the retrieval of the information from the database.
Interested to test it? Register for a free trial here.
For more information about DISGENET plus database, please visit https://disgenetplus.com/
Learn more about the current DISGENET plus database release
For licensing information, please contact us at info@disgenetplus.com
August 3rd, 2021: Release of the disgenetplus2r package
The package contains a set of functions to retrieve, visualize and expand DISGENET plus data. It allows to:
- Search by gene or multiple genes, using different identifiers
- Search one disease, or multiple diseases, using different identifiers
- Perform different operation with disease vocabularies
- Visualize the results of your queries using interactive networks, heatmaps, and other types of plots
For more information on the package functionalities and instructions on how to install and use it, please visit the disgenetplus2r documentation page.
July 20th, 2021: Release of version 16 of DISGENET plus
The version 16.0 of disgenet plus contains 1,203,188 gene-disease associations, between 22148 genes and 31107 diseases, disorders, traits, and clinical or abnormal human phenotypes, and 408,152 variant-disease associations, between 203,964 variants and 13,877 diseases, traits, and phenotypes, and over 34,000,000 disease-disease associations. DISGENET plus contains information that comprises 842,987 scientific publications.
June 23th, 2021: Release of version 15 of DISGENET plus
The version 15.0 of DISGENET plus contains 1,191,107 gene-disease associations, between 22,079 genes and 30,648 diseases, disorders, traits, and clinical or abnormal human phenotypes, 370,769 variant-disease associations, between 181,493 variants and 13,449 diseases, traits, and phenotypes, and over 34,000,000 disease-disease associations. DISGENET plus contains information that comprises 846,941 scientific publications.